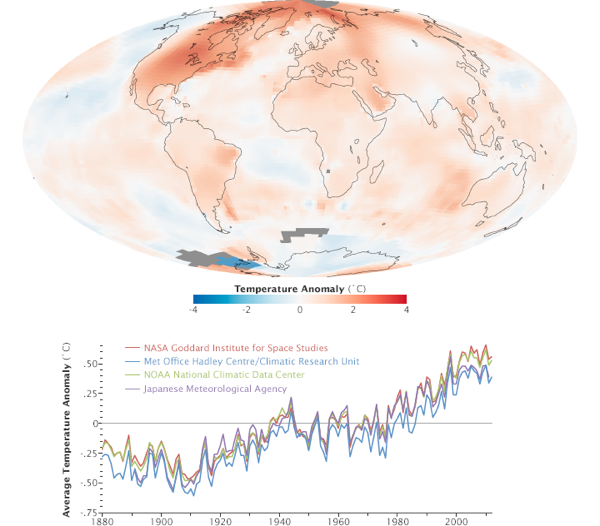
Scientists at NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) say 2012 was the ninth warmest year since 1880, continuing a long-term trend of rising global temperatures. The ten warmest years in the 132-year record have all occurred since 1998. The last year that was cooler than average was 1976.
The map at the top depicts temperature anomalies, or changes, by region in 2012; it does not show absolute temperature. Reds and blues show how much warmer or cooler each area was in 2012 compared to an averaged base period from 1951–1980. For more explanation of how the analysis works, read: World of Change: Global Temperatures.
The average temperature in 2012 was about 14.6 degrees Celsius (58.3 degrees Fahrenheit), which is 0.55°C (1.0°F) warmer than the mid-20th century base period. The average global temperature has increased 0.8°C (1.4°F) since 1880, and most of that change has occurred in the past four decades.
The line plot above shows yearly temperature anomalies from 1880 to 2011 as recorded by NASA GISS, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Climatic Data Center, the Japanese Meteorological Agency, and the Met Office Hadley Centre in the United Kingdom. All four institutions tally temperature data from stations around the world and make independent judgments about whether the year was warm or cool compared to other years. Though there are minor variations from year to year, all four records show peaks and valleys in sync with each other. All show rapid warming in the past few decades, and all show the last decade as the warmest.
_____________________________________________
The burning of wood is a major source of black carbon the world over.

Black carbon, or soot, is making a much larger contribution to global warming than previously recognised, according to research in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres..
Scientists say that particles from diesel engines and wood burning could be having twice as much warming effect as assessed in past estimates.
They say it ranks second only to carbon dioxide as the most important climate-warming agent.
Black carbon aerosols have been known to warm the atmosphere for many years by absorbing sunlight. They also speed the melting of ice and snow.
This new study concludes the dark particles are having a warming effect approximately two thirds that of carbon dioxide, and greater than methane.
Black carbon is said to be a significant source of rapid warming in the northern United States, Canada, northern Europe and northern Asia. The particles are also said to have an impact on rainfall patterns in the Asian monsoon.
No comments:
Post a Comment