Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.3 Earthquake hits western Xizang, China.
5.0 Earthquake hits North Island, New Zealand.
5.0 Earthquake hits southern Sumatra, Indonesia.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.3 Earthquake hits western Xizang, China.
5.0 Earthquake hits North Island, New Zealand.
5.0 Earthquake hits southern Sumatra, Indonesia.
Tropical Storms
In the South Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone Hellen is located approximately 240 nm north-northwest of Antananarivo, Madagascar.
Extremely dangerous Category 4 Tropical Cyclone Hellen is bearing down on Madagascar after an extraordinary burst of rapid intensification brought the cyclone from a 60 mph tropical storm to a high-end Category 4 storm with 150 mph winds in just 24 hours. Hellen is forecast to strike Madagascar as a very intense tropical cyclone at about 12:00 GMT on 31 March.
The La Réunion weather service has issued a warning: Hellen is likely to be one of the most powerful tropical cyclones ever seen over the northern channel since the satellite era (1967). the likelihood is increasing for an extremely dangerous tropical cyclone landfall over the northwestern coastline of Madagascar between cape Saint-Andre and Mahajonga. the RSMC tropical cyclone storm surge RWP has been run and shows phenomenal sea elevations in the area exposed to the northerly winds.
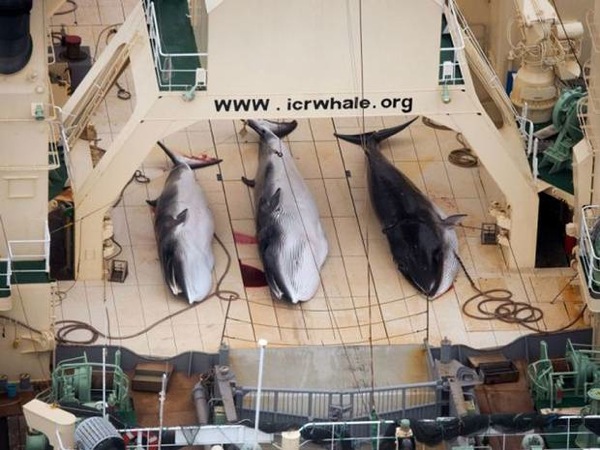
U.N. Court Orders Japan to Stop Whale Hunt
The UN’s top court ruled on Monday to temporarily halt Japan’s whaling program in Antarctic waters, in a case brought against the country by Australia and environmental groups.
Presiding Judge Peter Tomka at the International Court of Justice said that the court’s 16-member panel decided that Japan has not justified the large number of minke whales it takes under its program, while failing to meet much smaller targets for fin and humpback whales.
The court ordered a halt to the issuing of whaling permits until the program is redesigned.
Japan hunted around a thousand whales annually in what it claims was a scientific program.
But Australia and environmental groups accused Japan of attempting to manoeuvre around a moratorium on commercial whaling imposed by the International Whaling Commission in 1986.
While whale meat is becoming less popular in Japan, it is considered a delicacy by some, and meat from the hunt is sold commercially.

Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Guinea – update
As of 28 March, the total number of suspected and confirmed cases in the on-going Ebola haemorrhagic fever (EHF) outbreak in Guinea has increased to 112, including 70 deaths (Case Fatality Rate 62.5%). New suspected cases have been reported from Conakry (4 cases), Guékédou (4), Macenta (1) and Dabola (1) prefectures. The date of hospital admission of the most recent suspected case is 28 March.
Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Liberia
The Ministry of Health (MoH) of Liberia has provided updated details on the suspected and confirmed cases of Ebola haemorrhagic fever (EHF) in Liberia. As of 29 March, seven clinical samples, all from adult patients from Foya district, Lofa County, have been tested by PCR using Ebola Zaire virus primers by the mobile laboratory of the Institut Pasteur (IP) Dakar in Conakry. Two of those samples have tested positive for the ebolavirus. There have been 2 deaths among the suspected cases; a 35 year-old woman who died on 21 March tested positive for ebolavirus while a male patient who died on 27 March tested negative. Foya remains the only district in Liberia that has reported confirmed or suspected cases of EHF. As of 26 March, Liberia had 27 contacts under medical follow-up.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.4 Earthquake hits Fiji.
5.3 Earthquake hits Tonga.
5.1 Earthquake hits central Alaska.
5.0 Earthquake hits Hubei, China.
Tropical Storms
In the South Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone Hellen is located approximately 345 nm north-northwest of Antananarivo, Madagascar. Hellen, a low pressure area centred over the Mozambique Channel organized into Tropical Cyclone 21S (Hellen) on Friday afternoon.
NewsBytes:
8 Tornadoes Reportedly Hit Missouri, Southern Iowa late on Thursday.
Jakarta - Heavy rain that poured the city until Saturday (3/29) predawn, had caused two urban villages in East Jakarta, Kampung Pulo and Jatinegara, flooded. In addition, the overflowed of Ciliwung River and water from Bogor have inundated residents houses. The flood began to inundated 600 houses in Kampung Pulo since 3 am. The water level reached 30-100 cm. No one was evacuated.
Tanzania - One person was killed and fiver others went missing on Friday after floods triggered by ongoing heavy rains in many parts of Tanzania derailed a cargo train in the country’s central town of Mpwapwa. Mpwapwa district commissioner Christopher Kangoye said the floods swept away the locomotive engine of the cargo train that was pulling 11 petrol and diesel tankers and nine wagons with different types of cargo.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Etna (Sicily, Italy): Since the end of lava effusion 3 days ago, Etna has remained all quiet and the recent flow field is now slowly cooling down.
Ibu (Halmahera, Indonesia): Activity (effusive / explosive) continues at the volcano, which has an active lava dome. A new MODIS hot spot is visible on satellite data, suggesting this has recently increased.
Sinabung (Sumatra, Indonesia): The volcano remains active on a slowly decreasing trend, with little variation over the past weeks. The viscous lava lobe remains weakly alimented and continues to grow very slowly. An intermittent steam and sometimes light ash plume often rises up to about 14,000 ft (4.2 km) altitude. No new pyroclastic flows have occurred recently.
Poas (Costa Rica): Another small phreatic eruption occurred from the volcano's crater lake Friday morning.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.8 Earthquake hits the central Mid-Atlantic ridge.
5.6 Earthquake hits near the coast of Nicaragua.
5.4 Earthquake hits the northern Mid-Atlantic ridge.
5.2 Earthquake hits New Ireland, Papua New Guinea.
5.2 Earthquake hits near the east coast of Honahu, Japan.
5.1 Earthquake hits Hokkaido, Japan.
5.1 Earthquake hits the Greater Los Angeles Area, California.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Kermedec Islands.
5.0 Earthquake hits off the coast of Nicaragua.
Earthworms Stunted by Pesticide Use
Worms are struggling to cope with the use of pesticides, which a new study reveals alters both the physiology and behaviour of the important soil-aerating creatures.
A Danish-French research team studied earthworms that had been living for generations in soil sprayed with a fungicide.
"They spend a lot of energy on detoxifying, and that comes with a cost,” said researchers Nicolas Givaudan and Claudia Wiegand, whose report was published in the journal Soil Biology and Biochemistry.
And that cost is that they are less successful at reproducing and are much smaller than worms living in organic farming fields.
That means there are often two to three times more earthworms in unsprayed soil than in soil treated with pesticide.
Earthworms are important to the environment because they help in the decomposition of decaying leaves, as well as eat parts of fungus and bacteria.
Their burrowing activity brings air into the soil.
Earthworms living in ground treated with fungicide weigh half as much as those living in untreated fields.

Wildflower Blooming Expands Under Global Warming
Climate change has stretched the wildflower blooming season in the Rocky Mountains by more than a month, with half the flowers beginning to bloom weeks earlier than before.
But researcher David Inouye of the University of Maryland says that the flowering plants’ response to climate change is complex, with different species responding in unexpected ways.
Inouye began counting flowers in the Rockies in 1974, long before climate change was even on the scientific radar.
He and his students have since amassed an enormous amount of data on wildflower blooming, and say the blooming times are now changing rapidly.
Writing in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, he says that the peak time of wildflowers bursting into bloom has moved up five days per decade during his study.
But he says that as the bloom season lengthens, the plants are not producing more flowers.
The same number of blooms is spread out over more days, so at peak bloom there may be fewer flowers.

A Global Warming for the Ages Is Developing: UN
The head of the United Nations weather agency says that global warming has not changed and will continue for at least centuries due to the burning of fossil fuels by humans.
Michel Jarraud made the pronouncement as he presented the World Meteorological Organization’s annual review of the world’s climate.
The report concludes that last year tied with 2007 as the sixth-hottest since reliable records began over 150 years ago.
It also says that 13 of the 14 warmest years on record have occurred in this century.
“The warming of our oceans has accelerated, and at lower depths. More than 90 percent of the excess energy trapped by greenhouse gases is stored in the oceans," Jarraud told a news conference.
“Greenhouse gases are at record levels, meaning that our atmosphere and oceans will continue to warm for centuries to come. The laws of physics are non-negotiable,” Jarraud added.
Wildfires in Nebraska, USA
Firefighters are working to contain wildfires that charred crop fields, rangeland and pasture, including one that blackened nearly 11 square miles in central Nebraska.
The biggest fire, north of St. Paul, had been mostly contained Wednesday, but it flared up again Thursday and ignited some trees near the burned pastureland.
At least 17 fire departments were involved Wednesday when winds gusting over 40 mph helped spread the blaze. The fire destroyed one abandoned home and barn, and it killed several cattle but it was unclear how many. One firefighter also sustained minor injuries.
In southeast Nebraska, firefighters from several departments battled a fire that charred an estimated 300 acres north of U.S. Highway 34, near Union.
In northeast Nebraska, firefighters from Battle Creek, Humphrey, Norfolk, Madison and Stanton were dispatched to handle a wildfire along U.S. Highway 81 south of Norfolk.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Fuego volcano (Guatemala): The volcano's activity has dropped again a bit. During 27-28 March, 34 moderate explosions with ash plumes up to 800 m high were reported by the volcano observatory. Light ash falls occurred in areas to the west and many explosions were accompanied by shock waves. The recent lava flow, though, seems to be inactive again.
Karymsky volcano (Kamchatka) activity update: Activity at the volcano seems to have been on comparably high levels, since ash plume reports have become more frequent recently. VAAC Tokyo reported ongoing ash emissions with a plume drifting eastwards at estimated 7,000 ft (2.1 km) altitude.
Reventador volcano (Ecuador): elevated activity, lava flows and ash emissions. The volcano's activity has remained high since the beginning of the current eruptive phase since 25 March. Fresh lava continues to extrude at the summit crater, adding to the dome that had been active since 2011, and producing incandescent avalanches, small pyroclastic flows on its flanks and ash emissions. Seismic activity has remained at high levels, showing continuous tremor and emissions signals. IGPEN reports that the pyroclastic flows on the E, SE and S flanks have traveled up to 1.5 km from the summit. Additionally, there seems to be at least 2 lava flows that descend the south-eastern and eastern flank of the volcano, with fronts reaching approx. 500 m distance.
Shishaldin volcano (Aleutian Islands, Alaska): alert level raised, likely new lava dome growing incrater The Alaska Volcano Observatory raised the alert level for the volcano to Aviation Color Code ORANGE and Alert Level WATCH: "Elevated surface temperatures were detected in satellite data beginning on March 18 and have persisted to the present time. Analysis of this data shows that temperatures are consistent with the eruption of lava within the summit crater. The current activity appears to be confined to the deep summit crater and there have been no observations of lava on the flanks of the volcano or surrounding the summit crater. Web camera images, satellite data and pilot observations over the past week show only minor steam emissions from the mountain's summit crater. There has been no evidence of ash emission.
Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update
BOn 27 March 2014, the National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC) of China notified WHO of an additional laboratory-confirmed case of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.6 Earthquake hits La Rioja, Argentina.
5.4 Earthquake hits La Rioja, Argentina.
Tropical Storms
No current tropical storms.
NewsBytes:
Bangladesh - Storm hits 2 Sherpur upazilas. A norwester, accompanied by hailstorm, lashed 10 bordering villages in Nalitabari and Jhinaigati upazilas Tuesday night, damaging over 200 katcha houses and Boro seedlings and vegetables on a vast tract of land during its half an hour fury. The storm-hit villages are Sondhakura, Garokona, Gumra, Fhakhrabad, Haldi in Jhinaigati upazila, Samshchura, Hatipagar, Meshkura, Burunga and Kalapani in Nalitabari upazila.
Canada - Possible frost quake buckled shoreline at Kinbrook. A loud bang and subsequent mini-quake that rocked cabins at the north end of Kinbrook Island about five weeks ago is thought to be the result of a frost quake - the release of pressure built up by freezing water underground. The bang, or boom as some described it, was heard as far away as Lake Newell Resort, some six miles away.
Canada - The strongest Nor'easter of 2014 blasted Prince Edward Island, New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, Canada on Wednesday with wind gusts over 100 mph and up to a half meter (19.5") of snow, bringing travel to a standstill and causing power outages that affected about 17,000 customers in Nova Scotia.
USA -US mudslide death toll are expected to leap. Fatalities from last week's Washington state mudslide will rise "substantially" in the next two days, authorities say, with 90 people still missing.
Global Temperature Extremes
The week's hottest temperature was 113.0 degrees Fahrenheit (45.0 degrees Celsius) at N'guigmi, Niger.
The week's coldest temperature was minus 91.5 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 68.6 degrees Celsius) at Russia's Vostok Antarctic research station.
Temperatures were tabulated from the more than 10,000 worldwide synoptic weather stations. The United Nations World Meteorological Organization sets the standards for weather observations, and provides a global telecommunications circuit for data distribution.
Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Guinea - Update
The Ministry of Health of Guinea has today reported 4 laboratory confirmed cases of Ebola Haemorrhagic Fever (EHF) in the capital, Conakry. In addition, a fifth suspected case died without laboratory confirmation. Intensive case investigations are underway to identify the source and route of these patients’ infection, record their travel histories before arrival in Conakry and determine their period of infectivity for the purposes of contact tracing. Rapid Response Teams are carrying out these investigations and sensitizing health care workers and the affected communities about EHF to reduce the risk of further transmission.
The outbreak of the deadly Ebola virus said to have already claimed 63 lives in rural Guinea has now spread to the West African nation’s capital, Conakry, with the Health Ministry ringing the alarm and officials calling it a “threat to regional security.”
A total of four capital dwellers have fallen victim to the hemorrhagic fever – one of the deadliest viruses known to man. They are currently in quarantine, Reuters reports, citing local Health Minister Remy Lamah.
The origin of the outbreak in Conakry appears to be an old man who visited a place about 150km away from the previously-identified outbreaks. After his funeral, four of his brothers started showing similar symptoms, and were immediately quarantined.

Sanitary controls in neighboring countries are being activated, and border crossings have been closed to the north, with Mauritania, who only left two border posts open with Senegal.
The search for any vaccine or drug has thus far been hampered by the disease’s rarity. But health experts warn against obvious dangers, such as eating fruit bats. The animal is a local delicacy, but is a widely-known potential carrier of the disease. Bush meat is another cause for concern. Both types of meat have now been banned – as are public funerals, where proximity to the body is often the cause for the infection of groups of people.
The virus is incredibly contagious. It can spread through contact with contaminated corpses – as in the case of the last outbreak involving the four men – as well as direct contact with blood, feces and sweat. It’s not hard to picture a nightmare scenario in a country prone to hot weather.
But the spread itself can come much more unexpectedly as well. All it takes is one infected plane passenger, and the prospects are truly harrowing: the local Health Ministry in Canada's Saskatchewan province put a man and his entire family in quarantine after he exhibited disturbing symptoms upon arrival from Africa by plane.
The virus first appeared in 1976 in the DRC (formerly Zaire), and has since killed 1,500 people. Its name takes from a river in northern Congo.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update
On 20 and 21 March 2014, the Ministry of Health of Saudi Arabia announced an additional six laboratory-confirmed cases of infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update
Between 20 and 25 March 2014, the National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC) of China notified WHO of six additional laboratory-confirmed cases of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Etna (Sicily, Italy): During the night, the lava effusion and persistent mild explosive activity from the New SE crater ceased, after being nearly continuously active for over two months. If this is a true end or only a short pause to the latest eruptive phase which on 22 January remains to be seen. The tremor fell back to low levels in correspondence.
Karkar (Northeast of New Guinea): Several ash plumes at estimated altitude of 8,000 ft (2.4 km) were spotted during the past 2 days. This suggests a new eruptive phase could have started at the remote volcano.
Batu Tara (Sunda Islands, Indonesia): After a relatively long time with no spotted ash clouds, an ash plume was seen yesterday again on satellite imagery (VAAC Darwin). The remote volcano in the Fores Sea has been site of continuing strombolian activity since at least 2006. Some of the eruptions are strong enough to leave ash plumes that can be seen on satellite images.
Merapi (Central Java, Indonesia): A possibly strong eruption was reported from the volcano this afternoon (13:55 GMT). Satellite data showed an ash and SO2 plume drifting SW at estimated 32,000 ft (9 km) (VAAC Darwin). The plume is quickly dissipating, suggesting that the eruption was an isolated (possibly phreatic) explosion. No other details are at the moment available.
Marapi (Western Sumatra, Indonesia): The volcano erupted again yesterday afternoon at 16:15 local time, the volcano observatory post reported. It appears it was one of the largest explosions during the volcano's current phase of activity. Although the eruption was itself not visible due to cloud cover, the seismic signal showed a strong explosion that lasted 38 seconds and relatively "thick" ash fall occurred shortly afterwards in Batipuh and Tanahdatar districts until 17:45.
Dukono (Halmahera): Activity at the volcano continues to be intense. An ash plume was reported extending 80 nautical miles to the west at 10,000 ft (3 km) altitude this morning (VAAC Darwin).
Ubinas (Peru): The volcano's new lava dome continues to grow slowly within the crater. New field observations published yesterday in a detailed report showed that the lava dome is now approx. 120 m in diameter and has completely filled the inner pit left by the explosive activity in 2006 (as of 19 March). Visible glow (even in daylight) indicates very high temperatures. No explosions have occurred since the vent-clearing explosion on 14 Feb, but the volcano emits a significant plume of steam, SO2 gas and sometimes dilute ash. On 21 and 23 March, the steam-gas-ash plume rose 1800 m above the crater.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.0 Earthquake hits the Santa Cruz Islands.
5.4 Earthquake hits Halmahera, Indonesia.
5.4 Earthquake hits the north Indian Ocean.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Molucca Sea.
Global Warming Has Accelerated and Will Go On for Centuries
According to the head of the UN World Meteorological Organization, global warming has not reached a standstill - in fact, it has accelerated. Our planet will continue to warm for centuries to come, with disastrous consequences.
On Monday, the UN World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) issued its annual statement on the Status of the Climate. UN weather agency chief Michel Jarraud spoke out against climate skeptics, stating that "There is no standstill in global warming," and pointing to some of the extreme climate events of 2013.
"The warming of our oceans has accelerated, and at lower depths," Jarraud said. "More than 90% of the excess energy trapped by greenhouse gases is stored in the oceans.
"Levels of these greenhouse gases are at a record, meaning that our atmosphere and oceans will continue to warm for centuries to come. The laws of physics are non-negotiable."
Droughts, heat waves, rising seas, floods and tropical cyclones around the globe last year are just a glimpse of what may be coming in the future, the WMO's statement pointed out.
While skeptics point to natural phenomena like volcanoes or the El Niño or La Niña weather patterns as an explanation for the observed warming and disasters, Jarraud rejects their arguments. "Many of the extreme events of 2013 were consistent with what we would expect as a result of human-induced climate change," he said, pointing to the destruction wreaked by Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines.
Other 2013 examples that Jarraud pointed to were huge bush fires in Australia, winter freezes in the US south-east and Europe, heavy rains and floods in north-east China and eastern Russia, snow across the Middle East and drought in south-east Africa.

Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Guinea - Update
TThe total number of suspected cases in the ongoing Ebola haemorrhagic fever outbreak in Guinea remains 86. Two more cases died bringing total deaths to 62 (CFR: 72%). The cases are spread across three districts in south-east Guinea (Guekedou, Macenta, and Kissidougou districts). Seven of the cases are currently undergoing treatment in isolation units in Guekedou district. Investigations on reported cases in Liberia and Sierra Leone along the border with Guinea are ongoing.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update
On 23 March 2014, the National IHR Focal Point of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) notified WHO of an additional laboratory-confirmed case of infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Additional Outbreak of Foot-and-Mouth Disease in North Korea
The World Organization for Animal Health says deadly foot-and-mouth disease has spread to another farm in the North Korean capital Pyongyang.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Slamet (Central Java): Strombolian explosions of generally small size continue at irregular intervals. According to our correspondent Oystein, who visited the volcano last weekend, "the eruptions observed were fairly small (strombolian activity) and the interval between the eruptions ranged from 30min to 3 hours, during the periods I had clear views and were able to observe. No booming noises could be heard during the eruptions or incandescent material observed."
Fuego (Guatemala): (26 Mar) The volcano's activity has increased, INSIVUMEH and CONRED reported. The number of explosions rose to 8-14 per hour over the past days and the strongest ones produce ash plumes rising more than 1 km above the summit and drifted 12 km to westerly directions. Seismic data also show an increase in tremor (internal vibration). INSIVUMEH thinks that a new lava flow and / or another paroxysmal phase at the volcano could occur soon. The explosions at the volcano generated rumblings and shock waves that rattled ceilings and windows in villages Panimaché, Panimaché II, Morelia, Santa Sofia and others in the area at distances of more than 8 km.
Reventador (Ecuador): The volcano has entered a new eruptive phase since yesterday, Ecuador's Institute of Geophysics (IGP) reported. Starting from 15:00 local time yesterday, increasing tremor was registered and steady ash emissions were observed. At night, incandescent blocks could be seen and heard rolling down from the crater where probably a new lava dome has started to appear. Small pyroclastic flows descended on the eastern, southeastern and southern flanks of the volcano, probably as a result of re-mobilization of fresh lava and tephra deposits. These so-called secondary pyroclastic flows reached lengths of 500 m below the summit. IGP assumes the most likely scenario for the evolution of the new eruptive episode is that activity continues at similar levels for a while. So far, lava avalanches and pyroclastic flows have been confined within the caldera, near the flanks of the main cone. So far, no reports of ash falls became available from communities in the nearby areas, suggesting that the eruption is still small. An important hazard remains in the form of lahars (mud flows), which can be generated by re-mobilization of loose material during heavy rainfall and would most likely threaten the bed and banks of the Quijo river.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.5 Earthquake hits south of Fiji.
5.4 Earthquake hits southeast of the Ryukyu Islands off Japan.
5.1 Earthquake hits southern Peru.
5.1 Earthquake hits the Andreanof Islands in the Aleutian Islands.
5.0 Earthquake hits south of Fiji.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Bougainville region, Papua New Guinea.
Tropical Storms
In the Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone (tc) 17p (Gillian), located approximately 596 nm west of Learmonth, Australia, and is tracking south-southwestward at 06 knots.
Global Warming to Cause Food and Water Shortages, Reveals New UN Climate Report
As our climate shifts and changes, our food supplies may be in danger. Now, a new UN report has shown that global warming may already be causing irreversible damage to nature that could disrupt the world's supply of food.
Climate change is often viewed on a global scale, an many people see it as something that will happen far in the future. However, the new report reveals that the big risks and overall effects of global warming are far more immediate and local than you might think. Disease, drought, flooding, and hunger are all problems that will have to be dealt with.
"Climate change throughout the 21st century will lead to increases in ill-health in many regions, as compared to a baseline without climate change," stated the report,. "Examples include greater likelihood of injury, disease, and death due to more intense heatwaves and fires; increased likelihood of under-nutrition resulting from diminished food production in poor regions; and increased risks from food-born and water-borne disease."
Already we're seeing changes in the world. Coral reefs and Arctic ecosystem are experiencing irreversible changes. A mere warming of 2.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels could impact economic incomes of nations. While governments have agreed to help limit warming to less than 2 degrees, though, temperatures have already risen to about .8 degrees C.
Most notably is the fact that global food prices will rise. This, in particular, will have ripple effects across the globe. The report estimates that prices will rise between 3 and 84 percent by 2050 due to warmer temperatures and changes in rain patterns.
Scientist and more than 100 governments will meet in Japan from March 25 to 29 to look at, edit and approve the new report.
Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Guinea - Update
The Ministry of Health (MoH) of Guinea has notified WHO of a rapidly evolving outbreak of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in forested areas of south-eastern Guinea. As of 24 March 2014, a total of 86 cases including 59 deaths (case fatality ratio: 68.5%) had been reported.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update
On 20 March 2014, the National IHR Focal Point of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) notified WHO of an additional laboratory-confirmed case of infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Tropical Storms
In the Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone Gillian is located approximately 618 nm west-northwest of Learmonth, Australia.
NewsBytes:
Washington, USA - Officials now say as many as 176 people may remain unaccounted for after the 177ft (54m) wall of mud hit near the town of Oso, north of Seattle. Search crews have worked day and night, using helicopters and laser imaging. But officials admit they have little hope of finding survivors in the muck. The landslide "basically cut a mountain in two" and deposited it on the town below. Nothing in the path of the slide was still standing. "It's that absolute devastation that causes us all real pain." The official list of the missing stood at 176, but they did not think the final death toll would be so high, because some of those listed as unaccounted for would be found to be alive, and other names would prove to be duplicates.

Australia - The flash flood that hit Sydney on Monday afternoon has killed a man while two others were rushed to the hospital after being struck by lightning.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.7 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.7 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.4 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.3 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.3 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.3 Earthquake hits near the coast of Ecuador.
5.2 Earthquake hits Tonga.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Guinea
The Ministry of Health (MoH) of Guinea has notified WHO of a rapidly evolving outbreak of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in forested areas of south-eastern Guinea. As of 22 March 2014, a total of 49 cases including 29 deaths (case fatality ratio: 59%) had been reported.
Meanwhile a Canadian man is in hospital with Ebola-like virus. The Ebola virus is just one of the possible diagnoses. The man is in hospital in Canada with symptoms of a haemorrhagic fever resembling the Ebola virus.
The man had recently returned from Liberia in the west African region, currently suffering a deadly outbreak of an unidentified haemorrhagic fever. He is in isolation in critical condition in Saskatoon, the largest city in Saskatchewan province. A provincial medical official said there was no risk to the public.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Karymsky (Kamchatka): A volcanic ash plume was see on satellite imagery this morning at 10,000 ft (3 km) altitude and extending SE of the volcano, VAAC Tokyo reported. The volcano has been in a state of persistent, intermittent mild to moderate explosive activity at least since 1996.
Sakurajima (Kyushu, Japan): The volcano has been more productive again compared to most of this year so far. During the past 48 hours, VAAC Tokyo reported 8 explosions which ejected ash plumes to maximum of 8,000 ft (2.4 km) altitude.
Dukono (Halmahera): The volcano remains in elevated activity. Some of the (strombolian to vulcanian-type) explosions are strong enough to produce ash plumes spotted on satellite data. Yesterday evening and this morning, an ash plume could be seen drifting 50 nautical miles to the east.
Fuego (Guatemala): Strombolian explosions remain relatively frequent (6-8 per hour) and some of them have been at the higher end of the typical normal activity scale, with ash plumes rising up to 1,200 m above the crater. Incandescent material falling back from the stronger explosions cause spectacular incandescent avalanches on the upper cone. Moderately strong shock waves rattled windows in villages Panimache, Morelia, Sta. Sofía, and Panimache II. Loud degassing noises resembling jet-engines accompany the explosions.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.3 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits Fiji.
Tropical Storms
In the Western Pacific:
Philippines - The low pressure area (LPA), previously called tropical depression “Caloy,” could either intensify again once it passes over the open waters of the Sulu Sea or simply dissipate.
Forecasters said that based on current models, the LPA would linger within the Philippine area of responsibility (PAR) until Tuesday or Wednesday. While inside the PAR, it could either weaken further and dissipate or it could develop again into a tropical cyclone upon passing over open waters, where weather disturbances would usually gain strength. As of 4 p.m. Sunday, the LPA was estimated at 50 kilometers east of Dumaguete City and would bring moderate to occasionally heavy rains and thunderstorms over the Visayas.
In the Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone Gillian is located approximately 730 nm west-northwest of Learmonth, Australia.
NewsBytes:
Sixteen schools in the Upper Egyptian governorate of Aswan were evacuated on Sunday due to flooding. Egypt has witnessed unusually severe variations in weather in the last month, with heavy rains and sandstorms across the country. The inclement weather was the first of its kind in almost 20 years, according to Egypt's meteorological authority.
Tibet records rising temperatures and extreme weather
Global warming has reached the snow-capped Himalayas in south China's Tibet, with rising temperatures and more extreme weather, according to an official climate report.
The report on climate change and environmental monitoring in Tibet was published by the Tibet Climate Centre this week. The report is based on analysis of climate data collected between 1961 and 2013, showing that the average temperature in Tibet has been rising by 0.31 degrees Celsius every decade.
Tibet is the highest region in the mid-latitude regions, and seen as a barometer of global warming. Rising temperatures have been accompanied by increased precipitation, up by 6.6 millimetres every 10 years for the past five decades. There is also a trend of more severe extreme weather. Both the record low temperature of -36.7 degrees Celsius and the record high temperature of 32.3 degrees Celsius were logged in Tibet last year.
With the pace of global warming, the average temperature in Tibet is expected to rise by 1.96 degrees Celsius from 2011 to 2100, which would be mainly through a rise of winter temperatures. Warmer temperatures and increased precipitation are likely to add greenery to the plateau region.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.3 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.7 Earthquake hits the Fiji region.
5.5 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.4 Earthquake hits the Izu Islands off Japan.
5.3 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.1 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.1 Earthquake hits offshore Nayarit, Mexico.
5.1 Earthquake hits the Xinjiang-Xizang border region, China.
5.1 Earthquake hits Kepulauan Taluad, Indonesia.
Tropical Storms
In the Western Pacific:
Tropical depression Four [Caloy] is located approximately 225 nm northeast of Zamboanga, Philippines. The final advisory has been issued on this system.
'Caloy' makes landfall, leaves 1781 passengers stranded - Tropical Depression Caloy made landfall over Mindanao Saturday morning. "Caloy" weakened into a low-pressure area after making landfall over Surigao del Sur Saturday.
In the Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone Gillian is located approximately 420 nm east of Cocos Island, Australia.
NewsBytes:
USA - Huge Washington Landslide Kills Three and Dams a River - Three people were killed and eight injured in a mile-long landslide near Seattle that demolished at least six houses Saturday morning, blocked roads and dammed a river, bringing fears of a major flood.
Solar Power
The world’s largest solar thermal power plant that employs generating towers opened last month on the edge of California’s Mojave Desert.
The Ivanpaw Solar Electric Generating System consists of three towers that are surrounded by an array of more than 170,000 mirrors.
Those sun-following reflectors focus enough sunlight onto a small portion of the tower to generate enough power for 140,000 homes.
The facility, owned by NRG Energy, Google and BrightSource Energy, formally opened on February 17 and has a capacity of 392 megawatts.
But pilots flying over the array have complained of “nearly blinding” glare from the vast field of mirrors.
“In my opinion the reflection from these mirrors was a hazard to flight because for a brief time I could not scan the sky in that direction to look for other aircraft,” one pilot wrote to the Federal Aviation Administration.
Many other pilots said they have not had a problem flying over Ivanpah.
The Press-Enterprise reports that dozens of daily flights from Southern California to Las Vegas’ busy McCarran International Airport cross the California-Nevada border above or near the solar plant.
Some conservation groups have expressed concern about the plant’s threat to birds, which can be harmed or killed by the intense heat above the mirror arrays.
But proponents of this new solar energy facility say that the complex will reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 400,000 tons per year.

Large Dolphin Pod Dies After Becoming Trapped in Sea Ice
Canadian fisheries officials say about 40 white-beaked dolphins died after becoming trapped in jagged pack ice off the coast of Newfoundland.
The marine mammals struggled for days to stay alive in shallow water with no easy way to escape from ice that was hugging the shores of Cape Ray.
Footage taken by a resident and posted online shows the water tinted red with blood as the dolphins tried to get free.
White-beaked dolphins, which can weigh up to 660 pounds, are typically among the first marine mammals to arrive in the waters around Newfoundland as spring approaches, according to Wayne Ledwell of the region’s nonprofit group Whale Release and Strandings.
He says his records show more than 400 whales, dolphins and porpoises have been reported trapped in the ice around Newfoundland since the 1970s.
“Situations when marine animals become trapped in ice are very unfortunate, but do occur in the marine ecosystem (especially when ice conditions are extreme),” Larry Vaters of the Fishers and Oceans Department told reporters in an e-mail.
A fisheries expert said the unique geography and currents in the area form a natural trap for marine animals when there is heavy ice.

Ebola Outbreak Spreading in Africa
An Ebola outbreak has killed up to 59 people in Africa.
The outbreak, which has been going on in the southeastern region of Guinea since February, has infected at least 80 people so far, and may have spread to neighboring Sierra Leone, according to the government.The World Health Organization is sending a team to do additional testing, as well as sending more than 30 tons of medical supplies, including isolation chambers and medicine for treating fever, Reuters reported.
Ebola is a hemorrhagic virus that spreads through bodily fluids and can cause high fevers, diarrhoea, vomiting, and internal and external bleeding. There is no vaccine or cure for the virus and it can be fatal up to 90 percent of the time, according to the National Institutes of Health. Animals are thought to be the natural hosts for the disease, which has been transmitted to humans via chimpanzees, gorillas and monkeys.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Etna (Sicily, Italy): Mild strombolian activity is still continuing and ash emissions alternate with dense white vapour. A new effusive vent opened two days ago within the collapse scar alimented a lava flow but it seems no longer active today. The tremor does not show significant variations.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.3 Earthquake hits the Nicobar Islands off India.
There were no immediate reports of serious damage, and no tsunami warning was issued.
5.4 Earthquake hits the Nicobar Islands off India.
5.3 Earthquake hits the Nicobar Islands off India.
5.2 Earthquake hits the Gulf of California.
5.2 Earthquake hits southern California.
5.2 Earthquake hits the Nicobar Islands off India.
5.1 Earthquake hits western Uzbekistan.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Nicobar Islands off India.
5.0 Earthquake hits near the coast of northern Peru.
Tropical Storms
In the Eastern Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone (tc) 17p (Gillian), located approximately 890 nm northwest of Learmonth, Australia, and is tracking southwestward at 4 knots. Gillian has regenerated and is strengthening.
In the Western Pacific:
Tropical depression 04w (four), located approximately 428 nm southeast of Manila, Philippines, and is tracking west-northwestward at 07 knots.
Greenhouse Gas Levels Hit Another Milestone
Levels of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere have already surpassed a troublesome record set in May 2013, researchers said Wednesday (March 19). The week ending Tuesday, March 18, was the earliest to average more than 400 parts per million (ppm) of carbon dioxide, according to the Keeling Curve, one of the best climate records available. The 400-ppm milestone in 2013 was the first time carbon dioxide reached such a high level in human history.
The Keeling Curve is a continuous daily record of atmospheric carbon dioxide levels at Mauna Loa volcano in Hawaii, running since March 1958. That year, the greenhouse gas was at 313 parts per million. (Parts per million denotes the volume of a gas in the air; in this case, for every 1 million air molecules, 313 are carbon dioxide.)
While carbon dioxide levels have steadily climbed since 1958, every year there are seasonal variations. The yearly rise and fall reflects plant growth and death, which withdraws and releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide levels at Mauna Loa typically peak in May, but the high levels set in 2013 are appearing two months earlier this year. "We're already seeing values over 400. Probably we'll see values dwelling over 400 in April and May. It's just a matter of time before it stays over 400 forever," researcher Ralph Keeling said in a statement.
Nine US Fisheries Waste ‘Almost Half A Billion Seafood Meals,’ - New Report
What the United States wastes annually is nearly equivalent to what the rest of the world catches in the same time period.
A new report published by the nonprofit conservation group Oceana exposes nine of the "dirtiest" U.S. fisheries. When fishermen target a specific fish, it’s common for other species to get caught in their nets. This is known as bycatch, and it's a growing concern among nine U.S. fisheries.
“Anything can be bycatch. Whether it’s the thousands of sea turtles that are caught to bring you shrimp or the millions of pounds of cod and halibut that are thrown overboard after fishermen have reached their quota, bycatch is a waste of our ocean’s resources.” Depending on the type of fishing gear used, fishermen tend to catch everything from dolphins to sea turtles and sharks. These inadvertent catches are usually thrown overboard and tend to be injured, dead or dying.
The majority of bycatch tends to come from open ocean trawl, longline and gillnet fisheries. Researchers estimate that 20 percent of what fishermen catch in the U.S. is thrown away each year. This amounts to 2 billion pounds of wasted seafood. “The figures are astounding -- four fisheries discard 63 to 66 percent of everything they catch. If you can't quite grasp just how much that is, think of it this way: These nine fisheries waste almost half a billion seafood meals.”
The nine fisheries are: Southeast Snapper-Grouper Longline Fishery; California Set Gillnet Fishery; Southeast Shrimp Trawl Fishery; California Drift Gillnet Fishery; Gulf of Alaska Flatfish Trawl Fishery; Northeast Bottom Trawl; Mid-Atlantic Bottom Trawl Fishery Atlantic Highly Migratory Species Longline Fishery; and the New England and Mid-Atlantic Gillnet Fishery.
According to the report, the Southeast Snapper-Grouper Longline Fishery is the biggest offender, discarding 66 percent of whatever is caught. In one year, more than 400,000 sharks were caught attached to longlines. Despite the staggering numbers, the group maintains there's a solution to bycatch.
“The good news is that bycatch is a fixable problem. We need to accurately count everything that we catch, limit the amount of wasted catch in each fishery using science-based limits, and avoid catching non-target species by using more selective fishing gear.” Besides benefiting ocean life, reducing bycatch will help fishermen too. “By eliminating wasteful and harmful fishing practices we can restore and maintain fish populations that are essential to renewed abundance and healthy oceans, while also preventing the deaths of whales, dolphins, seals and sea turtles."
Monkey Fever Outbreak in India.
Monkey fever, a viral disease characterised by headache and haemorrhage, is sweeping through parts of Shimoga, Chikmagalur and Dakshina Kannada districts.
Also called the Kyasanur Forest Disease (KFD), it spreads through the bite of a forest tick which carries the disease-causing virus from monkeys and other hosts to humans. The Health Department has already recorded 74 cases of monkey fever, and has stepped up efforts to identify the affected, and take preventive measures in Thirthahalli and Hosanagar taluks of Shimoga and other affected districts.
Wildfires in Nepal
Wildfires have engulfed a vast swathe of forest land in Bara, Sarlahi and Rautahat districts in Nepal amidst gross apathy of government authorities, including district forest offices, to extinguish them.
According to locals, authorities have not taken initiatives to bring under control the infernos that have been raging for days.
“We used to see such wildfires in previous years too. I don’t know why forest officials are doing nothing to control the flames that have been destroying precious timber and the habitats of a number of wildlife species.”
Chief officer at the Chandranigahapur-based Rautahat district forest office, Baburam Bhandari, described the wildfires as a normal phenomenon.
He, however, expressed sadness at the inability to control the fires that have been raging for days.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Copahue (Chile/Argentina): SERNAGEOMIN raised the alert level of the volcano to orange yesterday after an increase in seismic activity. A pulse of volcanic tremor was detected that could indicate magma moving into the volcano's plumbing system. On the surface, no unusual activity has been seen at the volcano so far, except that an increase in SO2 emissions (approx 2,300 tons / day) was measured. This supports the idea that magma has risen under the edifice.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.7 Earthquake hits New Britain, Papua New Guinea.
5.4 Earthquake hits Antofagasta, Chile.
5.4 Earthquake hits New Britain, Papua New Guinea.
5.3 Earthquake hits New Britain, Papua New Guinea.
5.0 Earthquake hits near the coast of Nicaragua.
5.0 Earthquake hits south of Bali, Indonesia.
Tropical Storms
In the Eastern Indian Ocean:
Tropical cyclone (tc) 17p (Gillian), located approximately 834 nm north-northwest of Learmonth, Australia, and is tracking westward at 16 knots.
NewsBytes:
Afghanistan - Avalanche in Bamyan province of Afghanistan has claimed lives of at least five people.
India - Cyclonic storm in Meghalaya, India has claimed the lives of at least four people and injured 27 others.
Meteorite Gold Rush After South Korean Impacts
Residents of the South Korean city of Jinju have been scouring the surrounding hills and rice paddies in search of meteorites since a fireball shattered overhead earlier this month.
The country’s science institute confirmed that two rocks found in the area were “ordinary chondrite” meteorites of high iron composition.
That sent off a rush of treasure hunters, looking for stones that can be sold to collectors for tens of thousands of dollars each.
The stones are believed to have come from the same chunk of space debris that exploded while entering Earth’s atmosphere on March 9.
The government says it will designate any meteorites found as cultural assets to stop them from being taken out of the country.
The meteorites from Jinu are the first to be discovered on the Korean Peninsula since one was found during the Japanese occupation 71 years ago.
Global Temperature Extremes
The week's hottest temperature was 113.4 degrees Fahrenheit (45.2 degrees Celsius) at Damazine, Sudan.
The week's coldest temperature was minus 92.4 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 61.1 degrees Celsius) at Russia's Vostok Antarctic research station.
Temperatures were tabulated from the more than 10,000 worldwide synoptic weather stations. The United Nations World Meteorological Organization sets the standards for weather observations, and provides a global telecommunications circuit for data distribution.
Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update
On 19 March 2014, the National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC) of China notified WHO of an additional three laboratory-confirmed cases of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update
On 18 March 2014, WHO was notified of an additional two laboratory-confirmed cases of infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). One case was notified by the National IHR Focal Point of Kuwait and the other by the National IHR Focal Point of the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Etna (Sicily, Italy): Mild explosive activity continues at the New SE crater with little variation, but has now essentially become continuous. Weak lava effusion also continues to aliment small flows from vents at the eastern base of the cone. The tremor shows a fluctuating, but overall slowly increasing trend.
Hekla (Iceland): The volcano has drawn media attention and is being closely monitored as it is believed it is "ready" for a new eruption (although there are no current indications that one is imminent). A recent statement by Páll Einarsson, professor in geophysics at the University of Iceland, made headlines saying that "Hekla might eruption soon", because GPS deformation and strain measurements suggest that its shallow magma reservoirs have been filling up during the past years.
Colima (Western Mexico): The volcano produced a series of small ash puffs last night (23:00 GMT). VAAC Washington alerted of low ash plumes beneath flight level 150 (15,000 ft / 4.5 km altitude) drifting east from the volcano.
Poas (Costa Rica): Another moderately sized phreatic eruption from the crater lake of the volcano took place yesterday morning at 07:08 local time. The explosion ejected steam, water, mud and rocks to about 100 m height.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.7 Earthquake hits the South Sandwich Islands region.
5.6 Earthquake hits the Kermedec Islands.
5.1 Earthquake hits the Banda Sea.
5.0 Earthquake hits eastern New Guinea, Papua New Guinea.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Hindu Kush, Afghanistan.
Tropical Storms
In the Southwestern Pacific:
Tropical cyclone Mike is located approximately 618 nm southwest of Papeete, Tahiti. The final advisory has already been issued on this system.
NewsBytes:
Brazil - More than a month of flooding in northern Brazil has swollen rivers and driven thousands of people from their homes, authorities said on Wednesday.
Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update
On 17 March 2014, the Centre for Health Protection (CHP) of the Department of Health, Hong Kong SAR, China, notified WHO of an additional laboratory-confirmed case of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
Mystery Disease in Guinea.
An outbreak of hemorrhagic fever has killed at least 23 people in Guinea's southeastern forest region since February when the first case was reported, health authorities in the West African nation said on Wednesday.
At least 35 cases have been recorded by local health officials, said Sakoba Keita, the doctor in charge of the prevention of epidemics in Guinea's Health Ministry.
“Symptoms appear as diarrhoea and vomiting, with a very high fever. Some cases showed relatively heavy bleeding,” Keita said.
“We thought it was Lassa fever or another form of cholera but this disease seems to strike like lightning. We are looking at all possibilities, including Ebola, because bushmeat is consumed in that region and Guinea is in the Ebola belt,” he said. No cases of the highly contagious Ebola fever have ever been recorded in the country.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Slamet (Central Java): Mild strombolian activity occurs from the summit crater of Java's second highest volcano. A stronger explosion Wednesday morning at 08:47 local time produced an ash column rising about 2 km, according to a local press article. Light ash fall occurred in areas to the NW. The explosion was the largest in the current eruptive episode so far. The alert status of the volcano (raised to 2 out of 4 last Monday) was not changed,- apparently, no significantly larger eruptions are expected. During the past days, the volcano has been producing strombolian eruptions at rates of 1-2 per hour, with ash plumes typically rising 500-1500 m.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.9 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.6 Earthquake hits Taiwan.
5.4 Earthquake hits New Britain, Papua New Guinea.
5.2 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Hindu Kush, Afghanistan.
Tropical Storms
No current tropical storms.
Australia - Wild weather could be on way as Hadi spins back. The Mackay region could be in for some more wild weather later this week. While nothing is certain, the Bureau of Meteorology is predicting ex-Tropical Cyclone Hadi will spin its way back towards the east coast over the next few days.
A potential cyclone entered the Philippine area of responsibility before dawn on Wednesday. A low pressure area (LPA) was spotted 845 kilometers east of Mindanao as of 4 a.m. The LPA entered PAR at 2 a.m. and was moving west-northwest at 19 kilometers per hour. The LPA still has a slim chance of developing into a tropical cyclone. The LPA is forecast to bring cloudy skies with light to moderate rains and thunderstorms to Eastern Visayas, Central Visayas and Mindanao.
NewsBytes:
South Sudan - Floods displace South Sudan swamp communities. The start of the rainy season has brought flooding to Jonglei State’s swampy areas, where thousands of people are living in crowded conditions and lacking basic sanitation after already having been displaced by the violence that has swept the country.

Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update
On 14 March 2014, the Ministry of Health of Saudi Arabia announced an additional five laboratory-confirmed cases of infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Wildfire in Texas, USA
An out of control wildfire that started west of Higgins, Texas on Tuesday has spread to the Oklahoma State line and has spread over 20 miles. Oklahoma and Texas firefighters are battling the blaze in 25 - 35 mph gusty winds. The fire is expected to be brought under control shortly. No homes have been damaged.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Etna (Sicily, Italy): There have been no significant changes in activity. Mild strombolian explosions continue at the summit vent of the New Southeast Crater (NSEC) and lava emission continues to feed flows from the effusive vents at the eastern side of the cone.
Karymsky (Kamchatka): Intermittent strombolian to vulcanian explosions continue at the volcano. This morning, VAAC Tokyo reported an ash plume at 7,000 ft (2.1 km) altitude extending SE from Karymsky.
Sinabung (Sumatra, Indonesia): The volcano continues to be active with no significant changes, but an overall decreasing trend. Lava effusion feeds the viscous lava extrusion lobe on its southern flank, which has been mainly growing on its eastern side. No significant pyroclastic flows have occurred recently, only frequent smaller rockfalls. Small ash plumes continue to be regularly visible on satellite imagery. The most recent report by VSI shows that seismicity has decreased overall. Hybrid earthquakes, indicators of rock fracturing by magma moving into the system, have disappeared. This suggests that pressure and magma supply rate have dropped a lot and that the eruption could be ending in a near future.
Dukono (Halmahera): Intense explosive activity, probably strombolian-type, continue at the volcano. Darwin VAAC reports ash plumes at 8,000 ft (2.4 km) altitude extending 80 nautical miles to the SW.
Kilauea (Hawai'i): (17 Mar) Lava lake at Kilauea summit remains stable at a high point of 37m (124ft) and despite rainy and windy conditions over the weekend, the summit glow viewing is still clear and as bright as ever from the Jaggar Museum.
Santa María / Santiaguito (Guatemala): Activity remains essentially unchanged. Viscous lava flows are active on the E and SW sides of the Caliente dome. INSIVUMEH warns against the potential of hot lahars that the current and expected heavy rainfalls could trigger, re-mobilizing loose pyroclastic material that has been accumulating at the feet of the dome. The draining riverbeds of Nima I, Nima II, Samala, and San Isidro are the areas most at risk.
Fuego (Guatemala): Strombolian activity at the volcano has decreased a bit. Weak to moderate explosions occur at irregular intervals typically in the range of 1 hour, eject abundant incandescent lava to 100-150 m above the crater and generate avalanches on the upper slopes. The lava flow has stopped being active.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.6 Earthquake hits the South Georgia Island region.
5.3 Earthquake hits Taiwan.
5.3 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.2 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits New Britain, Papua New Guinea.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
Tropical Storms
No current tropical storms.
NewsBytes:
USA - The National Weather Service has reported record breaking snowfalls in New Jersey and around the nation’s capital.
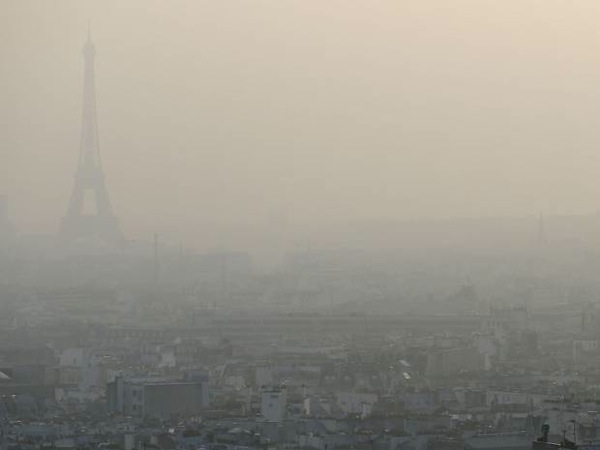
Pollution problems in Paris lead authorities to ban about half the cars Monday
Half the diesel and petrol cars in greater Paris will be banned from the road tomorrow in an attempt to reduce the health-threatening cloud of polluted air which has settled on northern France.
From 5am only odd-numbered cars will be allowed to drive in the Ile-de-France, unless they have electric or hybrid motors. Taxis, buses, emergency vehicles and cars carrying three people or more are exempted. All trucks are banned.
On Tuesday the ban will then apply to odd-numbered cars unless the weather changes. Foreign vehicles must obey the rules.
Since last Wednesday, a run of warm, windless days and cold clear nights has clamped a lid of warm air over northern France. Minuscule particles of pollution from car exhausts, industry and agriculture have accumulated under that lid to dangerous levels.

1,500-Year-Old Antarctic Moss Brought Back to Life
Moss frozen on an Antarctic island for more than 1,500 years was brought back to life in a British laboratory, researchers report.
The verdant growth marks the first time a plant has been resurrected after such a long freeze, the researchers said. "This is the very first instance we have of any plant or animal surviving [being frozen] for more than a couple of decades," said study co-author Peter Convey, an ecologist with the British Antarctic Survey.
There is potential for even longer cryopreservation, or survival by freezing, if mosses are blanketed by glaciers during a long ice age, the researchers think. Antarctica's oldest frozen mosses date back more than 5,000 years.
The findings were published today (March 17) in the journal Current Biology.
The moss comes from Signy Island, a small, glacier-covered island in the Drake Passage offshore of the Antarctic Peninsula. On Antarctic islands and the continent's coastline, thick, lush moss banks thrive on penguin poop and other bird droppings. The moss acts like tree rings, with layer upon layer of fuzzy clumps recording changing environmental conditions, such as wetter and drier climate shifts.
The moss resurrection came about after Convey and his colleagues noticed that old moss drilled out of permafrost on Signy Island looked remarkably fresh. The deeper layers didn't decay into brown peat (a type of decaying organic matter), as they would in warmer spots.
"In North America, you've got living moss on top of a dead peat base. It's black, wet sticky stuff," Convey told Live Science. "If you look at these cores [from Signy Island], the base is very well-preserved. They've got a very nice set of shoots."
To test whether the Antarctic moss would regrow, the researchers punched into the permanently frozen soil beneath the living moss, removing cores that contained frozen soil, ice and plants. To prevent contamination, they quickly wrapped the mossy cylinders in plastic and shipped them back to Britain at freezing temperatures. In the laboratory, the team sliced up the core and grew new moss in an incubator, directly from shoots preserved in the permafrost. They also carbon-dated the different layers, which provided an age estimate for revived moss shoots.
The oldest moss in the core first grew between 1,697 and 1,533 years ago, when the Mayan empire was at its height and the terror of Attila the Hun was ending in Europe and Central Asia. In the lab, this moss sent out new shoots from its rootlike "rhizoids," the researchers report. Because the growth comes directly from the preserved moss, and is the same species, it's unlikely that spores from elsewhere contaminated the samples, Convey said. (Antarctic mosses don't make spores.)
"We can't be certain there is no contamination, but we have very strong circumstantial evidence," he said. "Under a microscope, you can see the new shoot growing out of the old shoot. It is very firmly connected."
Many species other than mosses have unique survival strategies for the cold, such as hibernation in bears or bugs with built-in antifreeze — proteins that prevent destructive ice crystal growth. Others, including plants, simply endure freezing. Microbes and plant genetic material have been resurrected from ancient Siberia permafrost, more than 20,000 years old. But until now, scientists had hard evidence only of creatures surviving about 20 years without water or warmth, Convey said.
Researchers recently suggested that Antarctica's volcanoes radiate enough heat to provide refuges for life during Earth's coldest climate swings, when ice ages send the continent's glaciers far out to sea and ice covers the land. Species such as moss and bugs can't escape to warmer climates when the ice advances, because they're trapped by the vast Southern Ocean. Now, there's another survival mechanism for mosses, Convey said.
"In Antarctica, you've got survival challenges over a lot of different time scales," he said. "If you can get to 1,500 years, what's the possibility of surviving an entire glacial cycle?"
Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update
On 14 March 2014, the National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC) of China notified WHO of two additional laboratory-confirmed cases of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – update
On 26 February and 6 March 2014, the Ministry of Health of Saudi Arabia announced an additional two laboratory-confirmed cases of infection with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Poliovirus in Cameroon – update
In Cameroon, three additional wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1) cases have been reported with onset of paralysis on 6, 25, and 31 January 2014 from three new regions (North West, Adamaoua, and Centre) confirming continued WPV transmission and geographic expansion of infected areas following detection of four cases in October 2013. In total, seven WPV1 cases have now been reported from West, North West, Centre and Adamaoua Regions, with onset of paralysis ranging from 1 October 2013 to 31 January 2014. Genetic sequencing of WPV1 isolates suggests prolonged undetected circulation of poliovirus. Due to continued poliovirus circulation in Cameroon, gaps in surveillance, and influx of vulnerable refugee populations from Central African Republic, WHO is elevating the risk assessment of international spread of polio from Cameroon to very high.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
7.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
Chilean authorities said more than 100,000 people briefly evacuated some coastal areas as a precaution. Only minor damage was reported.
Chile is one of the world's most earthquake-prone countries. A magnitude-8.8 quake and the tsunami it unleashed in 2010 killed more than 500 people, destroyed 220,000 homes, and washed away docks, river fronts and seaside resorts.
The strongest earthquake ever recorded also happened in Chile, a magnitude-9.5 tremor in 1960 that killed more than 5,000 people.
6.2 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.5 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.1 Earthquake hits Mindanao in the philippines.
5.1 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.1 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Ceram Sea, Indonesia.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
5.0 Earthquake hits offshore Tarapaca, Chile.
Tropical Storms
No current tropical storms.
The remnants of what had been tropical cyclone Lusi were due to strike the Wellington region of New Zealand overnight, but the capital emerged relatively unscathed.
NewsBytes:
Torrential rains in South Africa have led to 32 deaths, 25 of which were drownings over the past two weeks.
Vanishing ice warning for 'Mountains of the Moon'
At 5 109 metres, Mount Stanley's jagged peak is the third highest mountain in Africa, topped only by Mount Kenya and Tanzania's iconic Kilimanjaro.
Ice on the Rwenzori mountain range is melting at "disturbing" rates, and within two decades Africa's equatorial peaks will be bare rock.
Ancient Greek geographer Ptolemy in Alexandria wrote of the snow-capped Rwenzoris around the second century AD, dubbing the mysterious peaks the "Mountains of the Moon", and identifying them as a source of the mighty White Nile.
But after centuries of wonder at the spectacle of snow on the equator, the ice is vanishing, bringing with it multiple challenges.
"The melting glaciers are another warning sign, a 'canary in the mine' of mankind's inability to contain climate change and its negative consequences," said Luc Hardy of Pax Arctica, an organisation that promotes awareness of the impact of climate change, and who led an expedition in January to the mountains.
"The melting of this unique African glacier is a major threat to local communities, with the obvious loss of sustainable water supplies.”
Reduced glacial river flows are already affecting agricultural production and cutting the output of hydroelectric power plants, said Richard Atugonza, from the Mountain Resource Centre at Uganda's Makere University.
British-American explorer Henry Morton Stanley was the first Westerner to sight the ice in 1889, but the dramatic sight of glinting snow in hot sunshine is fading fast, with maps showing the ice has shrunk from some seven square kilometres when they were first climbed in 1906, to just a single square kilometre today.
Fifty years ago, the glacier once began a stone's throw from the cliff-top Elena camp, where mountaineers shiver in basic huts before making a pre-dawn attempt to scale Stanley's peaks.
Now the ice lies almost an hour's tough scramble up a steep track on loose rocks along sheer cliffs.

Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
El Hierro (Canary Islands, Spain): What looks like a new swarm of earthquakes accompanied by strong harmonic tremor appeared on the southernmost seismic station at La Restinga. If it is not due to some local, human-induced work or malfunction, it suggests that the quakes are very shallow, since they don't appear on the signals of other stations. Whatever is happening there will probably become clearer soon. The latest earthquake swarm in the NE part of the island had more or less stopped during the past 24 hours. Some GPS stations showed 2-4 cm uplift during the weekend, which supports the idea of a new deep magma intrusion.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.3 Earthquake hits near the coast of northern Peru.
The earthquake struck about four miles from the coastal city of Sechura in northern Peru on Saturday, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. No damage or injuries were reported in the quake, which happened at a depth of six miles.
5.5 Earthquake hits Libertador O’Higgins, Chile.
5.2 Earthquake hits Taiwan.
5.0 Earthquake hits Kepulauan Barat Daya, Indonesia.
Tropical Storms
No current tropical storms.
NewsBytes:
Heavy rain in Oman has claimed the lives of at least four people over the last two days.
New Chemicals Found Eating Up Ozone Layer
Four mysterious and previously unidentified man-made compounds have been found that can destroy Earth’s upper-atmosphere ozone, possibly preventing the ozone hole from healing.
The production of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) gases came under restriction worldwide in the mid-1980s after the compounds were found to be creating the hole above Antarctica.
A total global ban on production came into force in 2010. But researchers say the four newly discovered chemicals, also powerful greenhouse gases, may be leaking from insecticide production and from solvents used in cleaning electronic components.
Scientists now caution that many others probably exist. “They might well add up to dangerous levels, especially if we keep finding more,” said Johannes Laube at the University of East Anglia.
Since the ozone-killing chemicals take decades to break down in the atmosphere, their impact on climate and the ozone hole is long-lasting.
Writing in the journal Nature Geoscience, researchers say the three new CFCs and one hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC) were detected in air bubbles trapped since the mid-1970s in the Greenland snowpack.
“I was surprised no-one had picked these up before,” said Laube.
Smog-Busting Drones to Clear Beijing Air
Outbreaks of smog around Beijing have become so acute that officials are testing a new, more efficient type of drone to be used to spray smog-clearing chemicals, primarily around airports.
The South China Morning Post reports that drones equipped with parasails can carry about 1,500 pounds of the unspecified smog-busting compounds, which are said to have the capacity to cleanse the air in a 3-mile radius.
The vehicles will reportedly spray chemicals that “freeze pollutants,” causing them to fall to the ground.
But environmental advocates warn that such a process would simply coat the city’s surfaces with still-toxic pollutants.
They add that the government is tackling the symptom rather than the root cause of pollution.
China has tested aircraft and fixed-wing drones to spray smog-dispersant chemicals for several years, but found those delivery vehicles to be prohibitively expensive.
New design of unmanned vehicle will spray chemicals that freeze floating particles, allowing them to fall to ground.

Drought and disease afflict desert region of Pakistan
As the death toll from the latest outbreak of poverty-driven diseases in Pakistan's Thar desert nears 100 children, experts are warning that corruption and a dysfunctional political system make a repeat of the disaster almost inevitable.
The desert region in Tharparkar, one of Pakistan's poorest districts, spreads over nearly 20,000 square kilometres in the country's southeast. It is home to some 1.3 million people, including a large population of minority Hindus.
Between March 2013 and February this year, rainfall was 30 per cent below usual, according to government data, with the worst-hit towns of Diplo, Chacro and Islamkot barely touched by a drop of water for months.
Experts warn of further disaster in poverty-hit area with 40 per cent Hindu population struck by lack of rainfall and death of livestock.
Life in the desert is closely tied to rain-dependent crops and animals, with farmers relying on beans, wheat and sesame seeds for survival, bartering surplus in exchange for livestock.
The drought is not the only reason for the recent deaths. Observers say they have come about as a result of endemic poverty, exacerbated by the drought and an outbreak of disease killing livestock.

Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.2 Earthquake hits near the coast of central Peru.
5.4 Earthquake hits south of Africa.
5.4 Earthquake hits the Nicobar Islands off India.
5.3 Earthquake hits the Volcano Islands off Japan.
5.3 Earthquake hits Kepulauan Mentawai, Indonesia.
5.2 Earthquake hits northern Sumatra, Indonesia.
5.2 Earthquake hits the Owen Fracture Zone region.
5.1 Earthquake hits the Philippine Islands.
5.1 Earthquake hits Tonga.
5.1 Earthquake hits the Carlsberg ridge.
5.1 Earthquake hits southeast of Easter Island.
5.0 Earthquake hits Zulia, Venezuela.
Tropical Storms
Ex-tropical Cyclone Gillian coming back to life over the Top End. Ex-tropical Cyclone Gillian is roaring back to life, the low pressure system expected to reform this afternoon and cross the Northern Territory coast of Australia. Ex-Tropical Cyclone Gillian had weakened to a remnant low pressure area after making landfall in the Western Cape York Peninsula of Queensland.
Remnants of Tropical Cyclone Lusi are likely to pass by Wellington and the lower North Island of New Zealand on Sunday. The storm may make weekend driving dangerous. Christchurch braces for 'mean and ugly' storm - What remains of severe Tropical Cyclone Lusi has an already saturated Christchurch putting emergency precautions in place ahead of this weekend's storm.
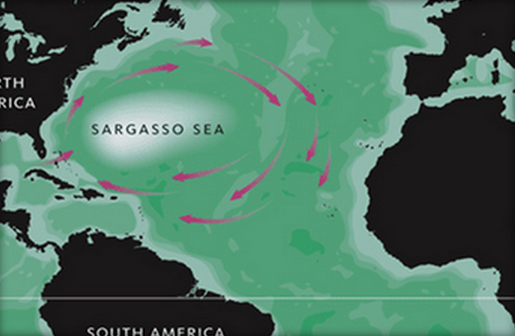
Threatened Sargasso Sea Ecosystem Earns Protections
Governments of several countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, Bermuda, the Azores and Monaco, have signed a declaration to protect the Sargasso Sea, according to a report by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
"This is a truly historic occasion," David Freestone, executive director of the Sargasso Sea Alliance, said in a statement. "It is the first time an international alliance has been formed to protect an iconic high seas ecosystem, using existing legal international frameworks,".
The "Hamilton Declaration on Collaboration for the Conservation of the Sargasso Sea" seeks to protect the area, whose abundant floating Sargassum seaweeds shield around 30 species of fish, as well as whales, dolphins and turtles, according to the IUCN report.
The Sargasso Sea is a calm patch of the North Atlantic Ocean isolated by ocean currents. The currents bring in algae and marine debris that help create and sustain the area's characteristic seaweed layer.
Despite being isolated by currents, the Sargasso Sea is subject to numerous ecological hazards, such as pollution, seabed mining and climate change, the report said. And, unlike some other ecologically vulnerable marine regions such as the Mediterranean Sea or the Southern Ocean, the Sargasso Sea is not officially protected by a specific regional organization.
Measels in the USA
New York City is currently grappling with a measles outbreak. Health officials have identified 16 cases of the highly contagious infectious disease, resulting in at least six hospitalizations, and are now warning unvaccinated individuals that they need to get their shots.
And New York isn’t the only place where measles — which was once so rare that it was virtually eradicated in the U.S. back in 2000 — is cropping up again. Within the past two months, health officials have also identified cases in the Boston, San Francisco, San Diego, and Dallas areas. Measles have also recently been reported in suburban areas in Connecticut and Illinois.
Just one case of measles can pose a huge public health threat, since it has the potential to be transmitted quickly. It can spread through the air when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. For instance, last month, thousands of California commuters were potentially exposed to the disease after an unvaccinated man with the measles rode public transportation.
Many of the measles outbreaks here in the U.S. originate after an unvaccinated individual has traveled abroad and contracted the disease there. Then, when they return to this country, they can spread measles among pockets of other unvaccinated people.
Officials say the underlying problem is that parents are not vaccinating their children.
Philippines: South Cotabato Declares Rabies Outbreak
In the aftermath of a human rabies death in Sto. Nino town in South Cotabato, Mindanao, provincial health officials declared a rabies outbreak.
Officials have launched a massive anti-rabies vaccination among pet animals in Barangay Poblacion of Sto. Nino in a bid to prevent the possible spread of the disease to other areas after a 44 year old man died of rabies.
Though a relatively rare cause of death in developed countries, 55,000 people die globally from this dreaded disease, mostly in Africa and Asia. That’s at a rate of one person every 10 minutes.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Cerro Negro de Mayasquer (Colombia): More than 11,000 micro-earthquakes at shallow depths were recorded beneath the volcanoes of Cerro Negro de Mayasquer and Chiles during the past few months, INGEOMINAS Pasto volcano observatory reported. The seismic record for Cerro Negro volcano goes only back to past November when a small network of seismometers and tiltmeters was installed, so it is not known whether the observed seismic activity is abnormal or part of the normal behavior of the volcano, which last might have erupted in 1936 and has only fumarolic activity at present. In absence of stronger signs of unrest, the alert level of Cerro Negro remains at green for the moment. The report mentions that a decrease in earthquakes was observed in the first months, while the numbers increased again this March. All quakes were tiny, not exceeding magnitude 1.2. Their hypocenters are located in a cluster a few km SE of Cerro Negro de Mayasquer and mostly between 3 and 5 km depth beneath the summit.
Ubinas (Peru): Weak ash emissions could be occurring at the volcano, recent webcam images suggest. VAAC Buenos Aires (one of the less busy VAAC centers) issued an alert in any case.
El Hierro (Canary Islands, Spain): A new swarm of earthquakes started yesterday. So far, almost 200 tiny quakes (none above magnitude 3 so far) have occurred in a broad N-S oriented area beneath the NE part of the island at around 18 km depth. A possible explanation includes a new magmatic intrusion at depth (magma accumulating at the lower crust-mantle boundary).
Kilauea (Hawai'i): (14 Mar) Spatter cones on the floor of Pu`u `O`o crater displayed persistent glow with an open lava pond within the collapsed northeast spatter cone!
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.3 Earthquake hits Kyushu, Japan.
5.5 Earthquake hits the Andreanof Islands in the Aleutian Islands.
5.4 Earthquake hits off the coast of northern California, USA.
5.1 Earthquake hits east of the South Sandwich Islands.
5.1 Earthquake hits Seram, Indonesia.
5.1 Earthquake hits offshore Coquimbo, Chile.
Tropical Storms
Tropical cyclone Lusi is located approximately 418 nm east of Noumea, New Caledonia.
New Zealand - Forecasters say the remains of Tropical Cyclone Lusi could dump 60mm to 100mm of rain on Christchurch this Sunday. The city is already saturated.
NewsBytes:
England - A series of cliff collapses at Birling Gap in East Sussex has prompted a warning to visitors to keep away from the edge. More tourists are expected this weekend because of the warm weather and the hope of seeing further erosion. On Tuesday, the high tide caused a severe fall in the cliffs after a 30ft crack appeared, resulting in a row of cottages ending up closer to the edge. The cliffs have already suffered seven years' worth of erosion, since January.
Lake Kariba - Incredibly Rare Tornado Sighted Over Lake Kariba, Zimbabwe.

How Dry Will It Get? New Climate Change Predictions
Global warming's crystal ball is clearing as climate models improve, and scientists now predict that some regions will see a month's less rain and snow by 2100.
The new rain and snow estimates indicate that subtropical spots — such as the Mediterranean, the Amazon, Central America and Indonesia — will undergo the biggest precipitation shifts in the coming decades. The number of dry days in these zones will rise by as many as 30 days per year, according to the study, published today (March 13) in the journal Scientific Reports.
"Looking at changes in the number of dry days per year is a new way of understanding how climate change will affect us that goes beyond just annual or seasonal mean precipitation changes, and allows us to better adapt to and mitigate the impacts of local hydrological changes," said Suraj Polade, a climate scientist at Scripps Institution of Oceanography in San Diego and lead study author.
The findings also suggest a rising probability of droughts and floods in the near future as annual rainfall becomes more variable.
"When you're increasing the variability of the climate, one year you can have a flood and the next year you can have a drought. You can also have an increase in extreme precipitation events, with a whole year's precipitation in just a few storms."
South Africa, Mexico and western Australia will go without rain for 15 to 20 more days per year, and California is likely to have five to 10 more dry days per year by the end of the century, the study found.
Some of the subtropical missing moisture will head north: The study predicts the Arctic will have 40 more wet days a year, but the South Pole will only get 10 more wet days per year.
Climate models suggest that midlatitude cyclones may shift north, while those that hit near the equator will likely stay their usual course.
There are also poleward shifts in the vast atmospheric patterns that control where rain falls. For example, the Hadley cell, the large-scale pattern of atmospheric circulation that transports heat from the tropics to the subtropics, has marched south during recent decades, moving the subtropical dry zone (a band that receives little rainfall) along with it. The northern and southern jet streams, which mark where cold and warm air meet, also seem to be creeping toward the poles. Their movement away from the equator suggests that the Earth's tropical zones are expanding, according to recent studies. The jet streams play an important role in moving moisture around the higher latitudes.
"We are looking at why this is happening," Polade said. "Earlier studies suggest that warmer regions will get wetter, while colder regions can get wetter or drier," he said. "The tropics are also getting wetter or drier, while the subtropics are drying."
Global Temperature Extremes
The week's hottest temperature was 112.3 degrees Fahrenheit (44.6 degrees Celsius) at Dampier, Western Australia.
The week's coldest temperature was minus 87.3 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 66.3 degrees Celsius) at Russia's Vostok Antarctic research station.
Temperatures were tabulated from the more than 10,000 worldwide synoptic weather stations. The United Nations World Meteorological Organization sets the standards for weather observations, and provides a global telecommunications circuit for data distribution.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.4 Earthquake hits south of Fiji.
5.2 Earthquake hits Tonga.
A second 5.2 Earthquake hits Tonga.
5.1 Earthquake hits Guerrero, Mexico.
5.0 Earthquake hits Tonga.
Tropical Storms
Tropical cyclone (tc) 18p (Lusi), located approximately 418 nm east of Noumea, New Caledonia, and is tracking southeastward at 13 knots. Lusi will sustain the current category 3 intensity for at least 12 hours before gradually weakening.
New Zealand’s Civil Defence and councils across the country are preparing for a battering as the tropical cyclone tacks toward New Zealand, bringing heavy rain and winds.
NewsBytes:
Flash flooding in Hail province in Saudi Arabia has claimed the lives of at least seven people. The authorities have ordered all schools in the region to close.
Avalanches and flash floods in Jammu and Kashmir in the last three days have claimed the lives of at least 16 people and injured 30 others. Heavy snowfall claimed the lives of three Nepalese workers when their stone quarry caved in near Kargil. Fatalities have been reported on both sides of the de-facto border between India and Pakistan. Complete power breakdown has been reported in Srinagar and the entire Kashmir valley as heavy snowfall damaged Jammu-Srinagar 220 kv and 440 kv transmission lines. A “high danger avalanche” warning has been issued in many parts of the region.
South Africa - Floods ahem inundated Limpopo Province as numerous rivers burst their banks after heavy downpours. The crocodile infested Mogol river has flooded the towns of Ellisras and Vaalwater.

Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – Update
WHO has been informed of an additional three laboratory-confirmed cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection. One case was reported from the United Arab Emirates (UAE) on 11 March and two cases from Saudi Arabia on 5 March.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
5.9 Earthquake hits the Bismarck Sea.
5.2 Earthquake hits Kepulauan Babar, Indonesia.
5.1 Earthquake hits the central Mid-Atlantic ridge.
5.1 Earthquake hits off the coast of Oregon, USA.
5.1 Earthquake hits eastern New Guinea, Papua New Guinea.
Tropical Storms
Tropical cyclone Lusi has now been upgraded to a category 2 storm as it heads east south east towards Fiji where a cyclone warning has now been issued. The cyclone now has winds near its centre of up to 130 kilometres an hour. By Wednesday afternoon the Fiji Weather Office said Lusi could be upgraded to Category 3.
The National Disaster Warning Centre in Thailand has issued a statement saying that a tropical storm was due to hit parts of the Northeast and the East hard on Tuesday and Wednesday.
Human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus – update
On 7 March 2014, the National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC) of China notified WHO of an additional laboratory-confirmed case of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
On 8 March 2014, the National Health and Family Planning Commission (NHFPC) of China notified WHO of three additional laboratory-confirmed case of human infection with avian influenza A(H7N9) virus.
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) – Update
On 20 February 2014, the Ministry of Health of Saudi Arabia announced two additional laboratory-confirmed cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection - somewhat belated report.
Roundup of Global Volcanic Activity:
Slamet (Central Java): (11 Mar) New eruptions were observed at Java's second highest volcano since yesterday evening. A series of explosions produced ash plumes rising 800-1000 m above the summit, the local observatory reported. This activity came after a steep increase in volcanic earthquakes from averages of approx 50 to more than 200 per day, volcanologist Mr Sudrajat from the local observatory told the press.
Kilauea (Hawai'i): Kilauea summit tiltmeters recorded minor fluctuations and the lava-lake rose to a measured 40m (131ft)- 20m (65ft) more until visible from the summit! The NE spatter cone complex continued to feed the Kahauale`a 2 lava flow 8km (5mi) NE of Pu`u `O`o, the farthest advance since January 2014!
Colima (Western Mexico): Mild effusive and explosive activity continue at the volcano. A recent overflight made by the Civil Protection's fire fighting department of Jalisco (UEPCBJ) showed no significant changes in the summit area of the volcano. A flat mass of viscous lava is slowly extruding and overspilling on the western and southern sides of the upper cone, causing incandescent avalanches sometimes visible at night. Intermittent explosions with ash emission also continue to occur.
Magnitude 5+ Earthquakes – Global
6.8 Earthquake hits the South Sandwich Islands.
5.4 Earthquake hits eastern New Guinea, Papua New Guinea.
5.1 Earthquake hits Vanuatu.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Kamchatka Peninsula, Russia.
5.0 Earthquake hits the Kermedec Islands.
Tropical Storms
Tropical cyclone Gillian is located approximately 162 nm east-northeast of Mornington Island, Australia. The final warning on this system has been issued by the joint typhoon wrncen Pearl Harbor hi. However, available model guidance suggests there is a possibility that the system will redevelop over the southern coast of the Gulf with moderate tropical cyclone intensity within the next 24 to 48 hours.
Fishermen in Australia pin hopes on Tropical Cyclone Gillian. Fishermen in the Gulf of Carpentaria are hopeful Tropical Cyclone Gillian will bring heavy inland rain, flushing out rivers to provide food for ocean fish.
Tropical cyclone Lusi is located approximately 408 nm north of Noumea, New Caledonia. Lusi has spawned warnings and watches in the Solomon Islands.
Tropical cyclone Hadi is located approximately 514 nm north of Brisbane, Australia.